Explain Any Differences Between These Two Values for Molar Volume
Therefore the molar mass 159994 gmol. Moles n mass mmolar mass M m O₂ 128 g O₂.
A Average Molar Volume from Trials 1 2 and 3 Lmol.

. Explain any differences between these two values for molar volume. Report with 3 significant figures b Ideal Molar volume from 4 Lmol. Calculate the theoretical value of the molar volume of an ideal gas at 215 C using the ideal gas law equation.
Most of the time it doesnt matter which unit of concentration you use. 1 mol CH 4. The discussion above of partial molar volumes used the notation VmA and VmB for the molar volumes of pure A and B.
It is the mass of a mole of a substance. If there is no difference explain why you should expect a difference. The partial molar volume of a pure substance is the same as the molar volume so we can simplify the notation by.
Both molarity and molality are measures of a chemical solutions concentration. Molarity and molality are both measures of the concentration of a chemical solution. This is your experimental value.
Where Vx is the molar volume in crystalline form and Vg is the obtained molar volume of the prepared glassfor a batch of boroalumino silicate glass with SrBa addition i got the value as 022how. Accurate to use in higher calculations. Use your experimental molar volume value from the first row in the above table to predict the volume occupied by 0415 mol of hydrogen gas under the same conditions of temperature and.
Volume 05 24 12 dm 3 Remember that 1 dm 3 1 000 cm 3 so the volume is also 12 000 cm 3 The equation can be rearranged to find the number of moles if. E1 E2. This is your theoretical value.
These were some important difference between molecular mass and molar mass. From this reaction equation it is possible to deduce the following molar ratios. M O₂ 2 15999 gmol O 31998 g O₂mol O₂.
The molar volume of a gas is 224 liters at STP standard temperature and pressure. This parameter is much more sensitive to structural differences between sweeteners than is partial molar volume and it best represents compatibility with water structure. 2 mol O 2.
The relationship between two solutions with the same amount of moles of solute can be represented by the formula c 1 V 1 c 2 V 2 where c is concentration and V is volume. Δ U Q W. It is denoted by ma.
V increases as T increases and vice versa V increases as n increases and vice versa The relationships among the volume of a gas and its pressure temperature and amount are summarized in Figure PageIndex 5. 5 percent difference. The symbol used for it is M.
It is a fairly simple sum to work out what 1 mole of helium He would occupy. C Explain any differences between these two values for molar volume. The primary difference between the two comes down to mass versus volume.
If there is no difference explain why you should expect a difference. At STP standard temperature and pressure this volume is 224 liters. 242 Lmol c Explain any differences between these two values for molar volume.
Almost any explanation must be based on differences in hydrogen bonding patterns with the two sub- stances. Molarity is the ratio of moles to volume of the solution molL while molality is the ratio of moles to the mass of the solvent molkg. That means that 01785 g of helium occupies 1 dm 3 at stp.
The heat capacity at constant pressure is. Molar Volume of an Ideal Gas Remember to report data and calculated results to the correct number. PV nRT where R 008206 L.
2 mol H 2 O. Volume increases with increasing temperature or amount but decreases with increasing pressure. It has a unit of the unified mass unit u or the atomic mass unit amu.
1 mol CH 4. For example at 273 K and 1 atmosphere pressure the density of helium is 01785 g dm -3. The heat capacity at constant volume is given by.
Different chemical elements have different molar mass values C -1201 g mol-1 Mg-243050 g mol-1 since they have a different number of positions in the nucleus. The molality describes the moles of a solute in relation to the mass of a solvent while the molarity is concerned with the moles of a solute in relation to the volume of a solution. 1 mole of every gas occupies the same volume at the same temperature and pressure.
Glycine and acetamide differ in formula only by an oxygen atom yet glycine which has the larger molecular weight has the smaller molar volume at pH 55 due to electrostriction. C V U T V. Molarity can be used to calculate the volume of solvent or the amount of solute.
The KZ8 of Q-galactose for example is - 208 x 103cm3mobar while. If there is no difference explain why you should expect a difference. Calculate the moles of O₂ in 128 g.
1 mol CH 4. Similarly this leads to having various unique molar mass values for chemical compounds. To compare this with the result of 102 ms2 from the first experiment you would.
There should be either heat Q or work W affecting the system. 1 mole of He weighs 4 g and would occupy 4. The atomic mass is the sum of the mass of protons neutrons and electrons.
G mol 1 is the standard unit for the molar mass. Suppose you obtained a value of 995 ms2 for g from a second experiment. View Homework Help - Lab 5 Molar Volume_ Assignment Sum2015 from CHM 113 at Arizona State University.
Less accurate than molecular mass. LatexPV nRTlatex where P is the pressure of a gas V is its volume n is the number of moles of the gas T is its temperature on the kelvin scale and R is a constant called the ideal gas constant or the universal gas constant. N O₂ 128 g31998 gmol 400 mol O₂.
Percent difference is used when comparing two experimental results E1 and E2 that were obtained using two different methods. Recall that U refers to internal energy. 2 mol O 2.
Combining these four laws yields the ideal gas law a relation between the pressure volume temperature and number of moles of a gas. In other words 1 mol of methane will produced 1 mole of carbon dioxide as long as the reaction goes to completion and there is plenty of oxygen present. At RTP room temperature and pressure this volume is 24 dm 3 liters We can also say.
1 mol CO 2. 2 mol O 2. 2 mol H 2 O.
Molecular mass of Ca OH2 74 atomic mass units. 1 mol CO 2. Mass of 1 mole of oxygen is 159994 grams.
Calculate the moles of NO that can be produced by 400 mol O₂ using the mole ratio between O₂ and NO from the balanced equation. This is your theoretical value.

Molar Volume Calculated Two Different Ways Youtube

Partial Molar Volume Example Youtube
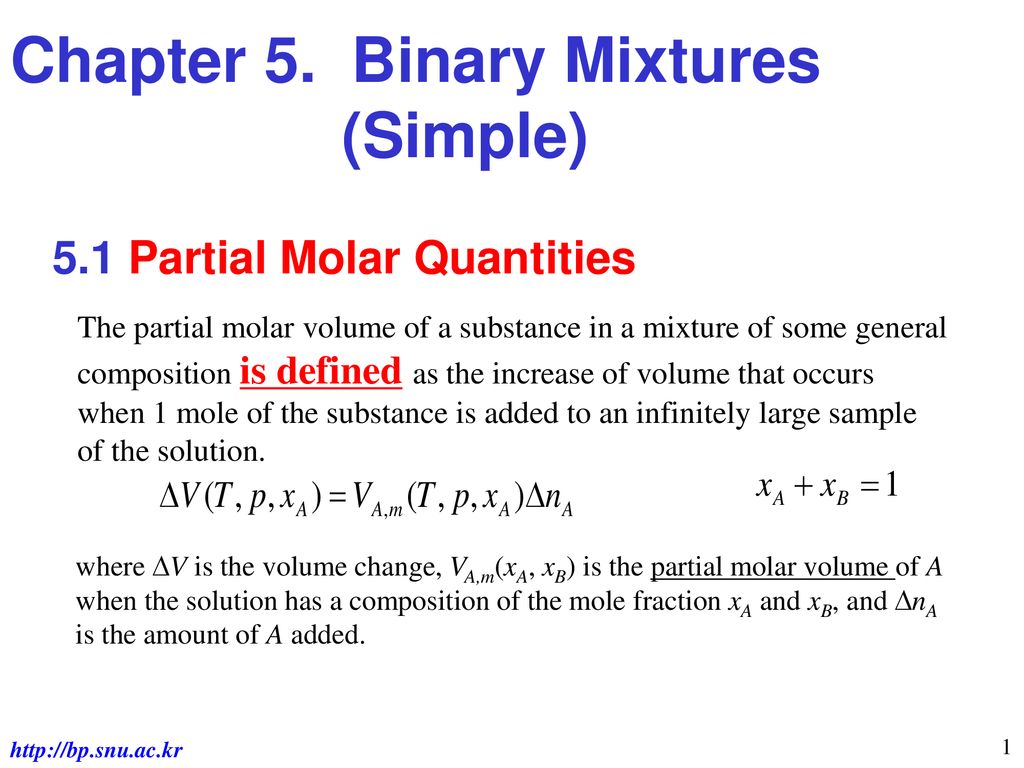
5 1 Partial Molar Quantities Ppt Download

Thermodynamics Gibbs Theorem And Partial Molar Volume Physics Stack Exchange

Mole And Gas Volume The Molar Volume Of A Gas Is Its Volume Per Mole Litre Mol 1 It Is The Same For All Gases At The Same Temperature And Pressure The

Molar Volume Is The Volume Occupied By 1 Mole Of Any Ideal Gas At Standard Temperature And Pressure Stp 0 C 1 Atmospheric Pressure Show That It Is 22 4 Litres Take R 8 31 J Mol 1 K 1

One Mole Of An Ideal Gas At Standard Temperature And Pressure Occupies 22 4 L Molar Volume What Is The Ratio Of Molar Volume To The Atomic Volume Of A Mole Of Hydrogen

Mole And Gas Volume The Molar Volume Of A Gas Is Its Volume Per Mole Litre Mol 1 It Is The Same For All Gases At The Same Temperature And Pressure The
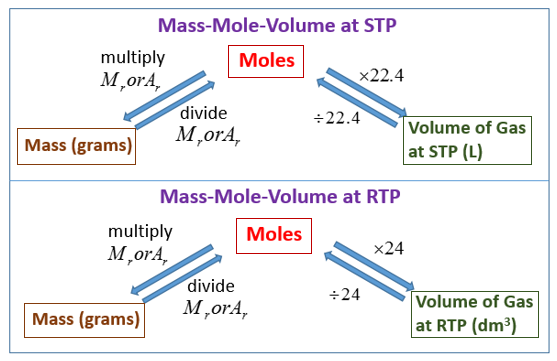
Molar Volume And Avogadro S Law Video Lessons Examples And Solutions
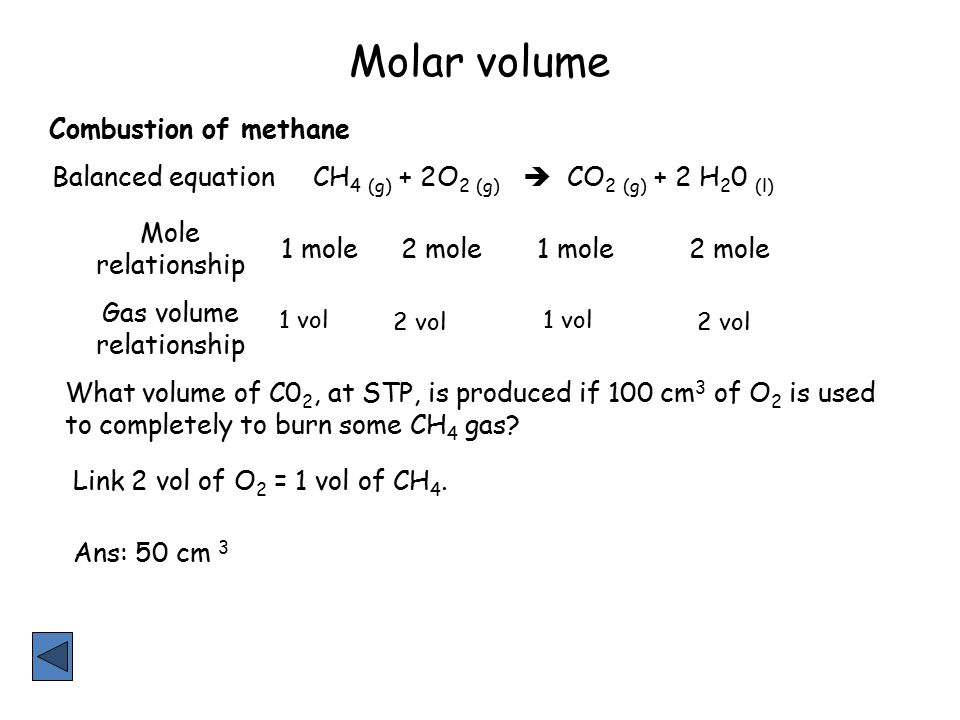
Mole And Gas Volume The Molar Volume Of A Gas Is Its Volume Per Mole Litre Mol 1 It Is The Same For All Gases At The Same Temperature And Pressure The

Question Video Recalling The Molar Volume Of A Gas At Rtp Nagwa

Thermodynamics Gibbs Theorem And Partial Molar Volume Physics Stack Exchange
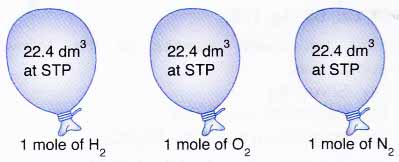
What Is The Molar Volume Of A Gas At Stp A Plus Topper

Molar Volume At Stp And Satp Youtube

Solved The Molar Volume Cm3 Mol 1 Of A Binary Liquid Mixture At Chegg Com

Question Video Calculating Molar Gas Volume At Standard Temperature And Pressure Stp Nagwa
Difference Between Molar Volume And Partial Molar Volume Definition Units Of Measurement Calculation Differences
Difference Between Molar Volume And Partial Molar Volume Definition Units Of Measurement Calculation Differences

Comments
Post a Comment